Maintenance is not just a checklist for compliance. It protects your engine, hydraulics, drivetrain, and braking system from avoidable wear. It also improves safety. Most serious failures give early warning signs. The goal of this guide is practical. You will know what to check and when to check it. You will know what actions to take when something looks wrong.
The best rule is the OEM rule. Use the HOWO manual as your primary schedule. Then use this article to make the daily work repeatable. This helps in dusty sites, high-load cycles, and frequent dumping operations.
Table of Contents
Maintenance Checklist and Schedule You Can Actually Follow
A good schedule is one you can complete consistently. If you make it too complex, drivers skip steps. If it is too vague, issues hide until they become downtime. The right approach is a short daily routine. In addition, add a post-shift routine. Finally, include a weekly and monthly plan that follows the OEM manual.
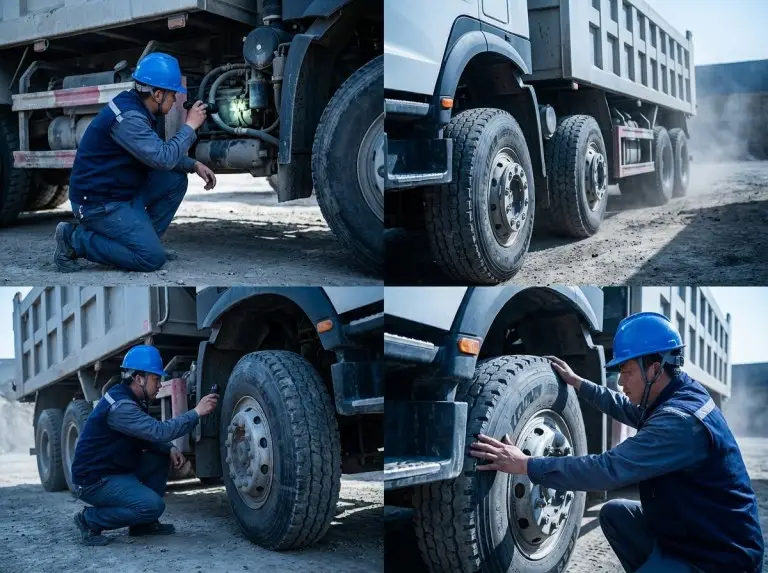
Daily Pre-Start Walkaround and Cab Checks
Start every shift with a walkaround. Look for changes from yesterday. Small leaks, loose fasteners, and heat damage show up early. However, look the same way every time.
Check the ground first. Fresh spots under the engine, gearbox, rear axle area, or hoist system signal an inspection. Do this before you move. If you see active dripping, do not start work. Confirm the source and the fluid level first.
Open the cab and check key indicators. Confirm there are no warning lights. Listen for unusual sounds at idle. If a new noise appears, treat it as a fault. Prove it normal first. Noise is often the first symptom of a lubrication or bearing issue.
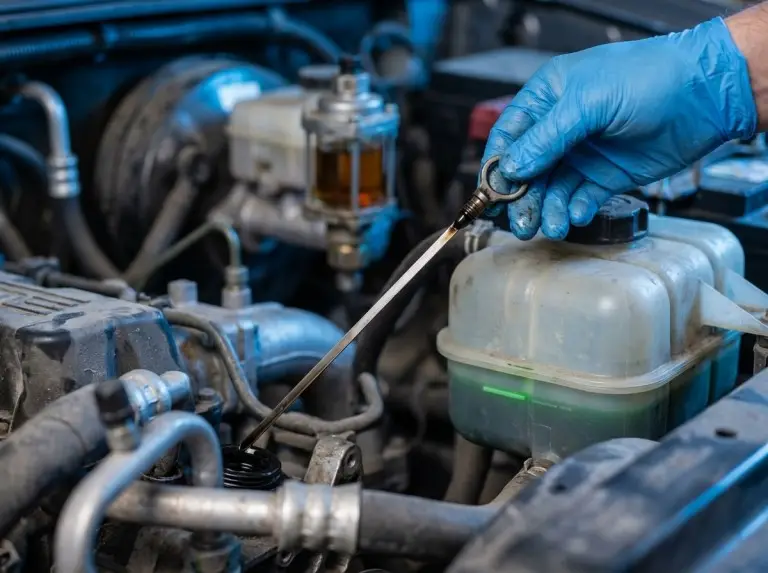
Next, check fluid levels. Engine oil, coolant, and hydraulic oil are the minimum set for daily work. The exact level marks and fluid grades must follow the OEM manual. Different configurations and engines use different specifications.
Finally, check tires and basic safety items. Verify tire pressure. Look for visible cuts and bulges. Confirm lights, signals, and horn function. Do this before entering traffic or a mixed job site.
Post-Operation Checks (Leaks, Heat, Damage, Cleaning)
End-of-shift checks reduce next-day surprises. They help you catch hot leaks. These appear after full working temperature.
Start with leaks again. After work, the hydraulic system and drivetrain have been under load. Look at hoses, fittings, and the area around the hoist cylinder and pump. Even minor seepage can become a blown hose. This happens under the next heavy cycle.
Check heat signs. Burnt smell or discoloration near hubs signal brake drag or bearing issues. Abnormal warmth around wheel ends does too. If you notice a heat pattern that does not match the other side, stop. Inspect before the next shift.
Clean the truck where it matters. Remove mud and debris from areas that trap moisture. Dirt buildup can hide cracks, loosened bolts, or hose rubbing points. Moreover, cleaning controls corrosion. This helps in wet or coastal environments.
Weekly and Monthly Tasks
Weekly tasks focus on wear items and systems. These degrade faster under heavy load cycles. For example, air filtration, fuel filtration, and brake system checks need weekly attention on dusty sites. If your conditions are mild, the OEM schedule may allow longer intervals. Do not assume.
Monthly tasks focus on deeper inspections. Check for loosening in suspension joints, steering linkages, and mounting points. Additionally, review recurring issues in your notes. Decide whether a pattern is emerging.
Do not overload the schedule with busy work. Pick tasks that catch high-cost failures early. Most fleets win on basics. These are oil, filtration, leak control, braking, and tires.
By-hours or By-km Service Logic
Use one primary metric. Keep it consistent. In heavy-duty dump work, hours can be more meaningful than distance. Idling and PTO/hoist cycles consume engine life. In transport-heavy work, kilometers or miles may fit better. The best answer is the one specified by your OEM manual and your duty cycle.
Avoid mixing intervals unless you state the rule clearly. A safe practice is to treat whichever comes first as the controlling trigger. If you cannot confirm a number from the manual, do not publish a hard value. Use the manual as the authority. Document your real operating conditions.
What to Record Each Shift
A short log is a maintenance multiplier. It creates traceability. Additionally, it makes troubleshooting faster. Furthermore, it prevents repeated small fixes that hide a real root cause.
Record three things. First, any top-up amount and fluid type. Second, any new noise, vibration, or warning indicator. Third, any leak location, even if it looks minor. When you see the same note three times, it is no longer minor.
If your site uses multiple drivers, shift logs protect the truck. The next operator should not discover problems the hard way.
Key System Maintenance Best Practices
Most failures come from a few predictable causes. Low or degraded fluids, contamination, heat, and loose connections are at the top. The sections below focus on the checks that control those risks.
Engine Oil and Filtration
Engine oil health controls engine life. Keep the oil at the correct level. Check it frequently. Do this in dusty or high-load operations. Low oil accelerates wear. It can cause severe damage. Too much oil raises temperature. It contributes to leakage and aeration.
Oil quality matters as much as oil level. If the oil looks diluted, heavily darkened too early, or smells burnt, treat it as a warning sign. Therefore, shorter intervals may be required in high dust, high idle, or extreme heat.
Filters are part of the lubrication system. Replace the oil filter on the correct schedule. Do not extend it beyond the oil interval without OEM guidance. A clogged or poor-quality filter can restrict flow. It reduces protection.
When you change oil, use a repeatable method. For example, warm oil drains better. Confirm the correct refill volume for your engine model. Then, recheck level after circulation. Do not check immediately after pouring.
Cooling System
Overheating shortens engine life fast. Check coolant level daily. Inspect hoses and clamps regularly. A small coolant leak can become a loss-of-coolant event. This happens in one heavy pull.
Keep the radiator and airflow path clean. Dump trucks work in dust. Fins clog easily. If you see rising operating temperatures over time, do not ignore it. Clean the cooling package. Verify fan operation and belt condition.
Never rely on water alone unless the OEM allows it for emergency use. Correct coolant mix supports corrosion control. It provides freezing and boiling protection. Follow the manual for coolant type and service interval.
Fuel System
Fuel contamination causes power loss and injector damage. The fix is discipline in filtration and water control.
Inspect fuel lines and fittings for seepage and rubbing points. Replace damaged hoses early. Keep an eye on filter change intervals. Do this if your fuel source quality varies.
If you have water separation capability, use it. Drain water when needed. Record it. Water in fuel is a repeat offender. If you see it repeatedly, address storage and supply practices at the site.
Drivetrain and Rear Axle
Drivetrain lubrication is not optional. Keep gear oil at the correct level in the transmission and axle system. Check it on a routine schedule. Low gear oil leads to early wear. Severe cases can cause overheating and component damage.
Rear axle and wheel-end systems are under heavy torque in dump work. If your configuration uses reducers, treat their oil level checks as a critical maintenance point. Use the correct gear oil grade and viscosity specified for the axle system. Do not guess. The wrong oil can change film strength and thermal behavior.
Use the differential lock correctly. Differential lock is for low-traction situations. Use it where a wheel is slipping and you cannot drive out. Engage it only when needed and at low speed. Once you are out of the slippery or muddy section, disengage it immediately. Driving on normal traction with the lock engaged can cause severe tire wear. It can cause mechanical damage.
Avoid overload. Dump trucks are designed around a rated load. Chronic overload and load concentration increase stress on the axle housing and drivetrain. You may still move the load. But you will pay with deformation, cracks, and premature failures.
Hydraulic Hoist System
The hoist system is the dump truck’s working tool. Hydraulic issues cause common downtime on job sites.
Start with the basics. Keep hydraulic oil at the correct level. Use the correct type. Low oil can introduce air. It reduces lifting force. It causes erratic operation. Overfilled oil can foam and leak.
Inspect hoses and fittings frequently. Look for cracks, abrasion, bulges, and wetness at fittings. Hose rubbing points are predictable. If a hose touches metal, it will fail sooner than you expect.
Listen to the pump. Unusual noise can mean air in the system. It can mean restricted flow or wear. If the bed lifts slowly or hesitates, do not keep forcing cycles. Stop and check oil level. Check filter condition. Check whether air may have entered.
Bleeding air can be necessary after service or a low-oil event. Follow the correct procedure from the OEM manual. Improper bleeding can introduce more air. It can stress components. If you are unsure, treat it as a service task. Do not treat it as a field experiment.
Electrical Basics
Electrical faults create mystery downtime. Many of them are simple connection problems.
Check battery terminals for corrosion and tightness. Clean them when needed. Ensure protective measures are in place. Inspect wiring harness routes for chafing and heat exposure. A rubbed wire can trigger intermittent faults. These waste hours.
Confirm charging health if you see repeated low-voltage symptoms. Dim lights, slow cranking, or repeated battery failures are signals. Inspect the alternator, belt drive, and grounding points.
Tires, Brakes, Suspension, and Steering Safety Checks
These systems protect people first. They protect uptime second. Dump trucks operate under heavy loads. They work on uneven terrain. They do frequent stop-start cycles. That combination accelerates wear.
Tires and Wheels: Correct tire pressure improves stability. It improves braking and fuel efficiency. Under-inflation causes heat buildup. It causes uneven wear. Over-inflation reduces contact patch. It can worsen traction on rough surfaces.Inspect tread and sidewalls for cuts, bulges, and embedded debris. Replace damaged tires promptly. This prevents blowouts. If you see uneven wear, do not just rotate and forget. Uneven wear can signal alignment issues. It can signal suspension wear or load imbalance.Wheel fasteners matter. After wheel service and during early life periods, recheck wheel nut torque. Follow OEM procedure. Loose fasteners can damage wheel ends. They create high-risk failures.
Brakes: Brakes are a critical safety component. Inspect pads and discs for wear and damage. Do this on a routine schedule. If pads are worn beyond minimum thickness, replace them. Do not wait for metal-to-metal contact. It can damage discs. It reduces braking capacity.If your truck uses air brakes, check for air leaks. Look in lines, tanks, and fittings. A slow pressure drop can become a no-brake event in a single shift. Always monitor air pressure build. Monitor response behavior.Test braking response in a controlled, safe area. If braking feels weak, uneven, or delayed, stop work. Inspect before carrying a full load. Brake issues under load are dangerous.
Suspension and Steering: Suspension and steering keep the truck stable. Worn components reduce control. They accelerate tire wear.Inspect suspension parts for looseness, cracks, and damaged bushings. Look for shifted components. Look for abnormal movement. Steering systems should be checked for leaks. Check for damaged boots and free play.If handling changes suddenly, do not assume it is just the road. A new pull, vibration, or steering looseness is a signal. Inspect immediately. Many steering failures give warning signs before they become critical.
Common Symptoms, Likely Causes, and When to Stop Work
When a dump truck shows a symptom, prevent escalation. Use a consistent troubleshooting path. Start with safety. Then check fluids. Then check visible mechanical causes. If the symptom suggests imminent failure, stop work.
Leaks
If you see active dripping, stop and inspect. First identify the fluid. Engine oil is usually dark and slippery. Coolant often leaves a colored residue and sweet odor. Fuel has a distinct smell. It is a fire risk. Hydraulic oil is typically clean to amber. It often appears near hoses and cylinders.
Then check level. A leak with a low level is not a finish-the-shift issue. It is a downtime issue now. Running low oil or low coolant can destroy expensive components.
Abnormal Noises
New noises are meaningful. A knock or sharp metallic sound from the engine area is a stop signal. A whining noise from driveline areas can indicate lubrication or bearing issues. A cavitation-like noise from the hydraulic pump often points to air. It points to low oil or restriction.
Do not test longer to see if it goes away. Noise gets worse under load. Instead, reduce load. Stop and check fluid levels. Check obvious mechanical connections.
Overheating and Power Loss
Overheating is a stop-work trigger. This happens when it exceeds normal operating range. Or when it rises rapidly. Check coolant level and visible leaks. Inspect radiator blockage and fan function. If power loss accompanies overheating, do not keep pushing. You risk severe engine damage.
Power loss without overheating often points to fuel contamination. It points to restricted air intake or filter issues. Start with filters and intake restrictions. Then check for fuel line leaks or water presence. Do this if your system supports separation.
Poor Braking or Air Pressure Drop
If braking performance changes, stop work. Do not carry heavy loads until the system is verified.
For air systems, watch pressure behavior. Slow build, frequent compressor cycling, or pressure drop suggests leaks. It suggests system faults. Audible air leaks are not acceptable. Fix them before returning to service.
Slow or Unstable Dumping
If the dump bed lifts slowly, shakes, or refuses to hold, stop and inspect. First check hydraulic oil level. Then inspect for visible leaks at hoses, fittings, and cylinders.
Unstable dumping can be a safety hazard. If the bed behavior is erratic, do not stand near the dump body. Do not keep cycling the system. Correct the issue with proper inspection and service steps.
Conclusion
A HOWO dump truck stays reliable when maintenance is routine, not reactive. At Genron, we recommend a simple system. Use daily checks and post-shift checks. Follow an OEM-led preventive schedule. Focus on fluids, filtration, leak control, brakes, tires, and the hoist system. This approach reduces downtime. You catch faults when they are still small.
If you run in dust, heavy loads, and frequent dump cycles, discipline matters more than complexity. Keep records. Fix leaks early. Treat abnormal noise, overheating, and braking changes as stop-work signals. With consistent maintenance, your HOWO dump truck will deliver longer service life. It will provide safer operation. It will give lower total cost over time.
Further Reading:HOWO Truck Maintenance Guide
FAQ
What are the most critical components to inspect daily on a HOWO dump truck?
The most critical daily checks are fluids, leaks, tires, and basic braking readiness. Check engine oil, coolant, and hydraulic oil levels. Then look for fresh leaks under the truck. Inspect tire condition and inflation. Confirm no warning indicators are active before working under load.
How often should engine oil be replaced for heavy dump work?
Follow the OEM manual as the primary rule. Shorten intervals if your duty cycle is dusty, high-load, or high-idle. If you cannot confirm an interval for your exact engine model, do not rely on generic numbers. Use whichever comes first logic when the OEM provides both hours and distance triggers.
What are common brake pad wear signs, and when should pads be replaced?
Replace pads when they approach the OEM minimum thickness. Or when they show cracks, glazing, or abnormal scoring. If braking feels weaker, uneven, or noisy under normal conditions, treat it as an inspection trigger. Waiting too long can damage discs. It reduces braking capacity under heavy loads.
How can we improve fuel efficiency through maintenance without changing the truck setup?
Maintain correct tire pressure. Keep filters on schedule. Prevent fuel contamination. Clean air intake and healthy filtration reduce pumping losses. They improve combustion stability. Fix leaks and dragging brakes early. They silently increase fuel burn.
What is a practical tire rotation and wear-control approach for dump trucks?
Rotate and inspect tires on a consistent schedule. Define it by your OEM and your work conditions. Use rotation to manage wear. But also diagnose the pattern. Uneven wear often points to alignment, suspension wear, or load imbalance. This needs correction, not just rotation.
How do we check for hydraulic fluid leaks and prevent hoist downtime?
Inspect hoses, fittings, and cylinder areas for wetness, droplets, or stains. Do this before and after work. Track hydraulic oil top-ups. Investigate repeated loss. If the pump becomes noisy or the bed lifts slowly, check oil level first. Stop cycling until the cause is confirmed.